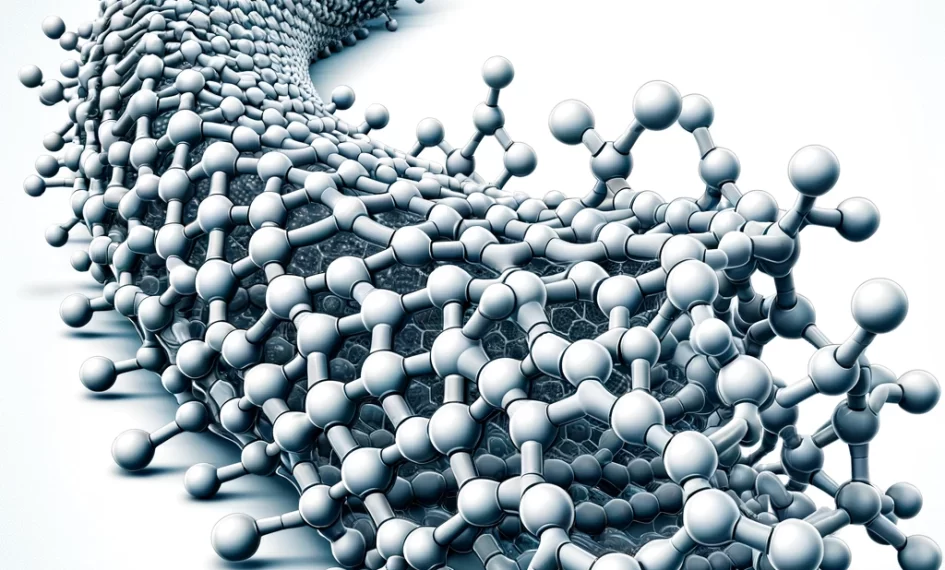
- Definition: A polymer is a large molecule, or macromolecule, composed of many repeated subunits. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds. Polymers, which include plastics, DNA, and proteins, are essential in both natural processes and manufactured goods.
- Etymology and Origin:
- The word “polymer” is derived from the Greek words “poly,” meaning “many,” and “meros,” meaning “part” or “segment.” Thus, it literally translates to “many parts.”
- The term was first used in the 19th century to describe organic compounds with identical molecular formulas but different properties, a concept known as isomerism.
- The modern understanding of polymers, as large molecules built from repeating structural units, developed in the early 20th century with advancements in organic chemistry. This concept revolutionized the materials industry and led to the development of numerous synthetic polymers.
Polymer: Deciphering Its Definition and Greek Roots

1 comment