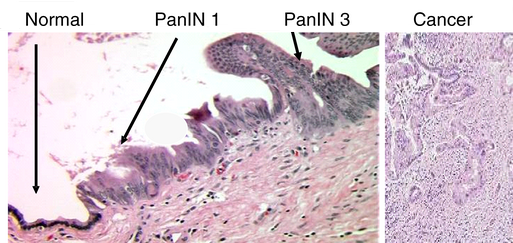
Definition:
Pathology is the medical science that studies the causes, effects, and nature of diseases. It involves examining tissues, organs, bodily fluids, and autopsies to diagnose illness, understand its progression, and determine the impact on the body. Pathology bridges clinical practice with the biological sciences, playing a crucial role in diagnosis, research, and understanding the mechanisms of disease.
Etymology & Origin:
Derived from the Greek words “pathos” meaning “suffering” or “disease” and “-logy” meaning “study of,” pathology literally translates to the study of suffering. It emphasizes the focus on understanding diseases and their effects on the human body. The term has been part of the medical vocabulary since the early 17th century, reflecting the discipline’s long-standing role in medicine.
Examples:
- Surgical pathology involves the examination of tissues removed during surgery to help diagnose disease and determine treatment.
- Clinical pathology focuses on the analysis of blood, urine, and tissue samples to diagnose diseases.
- Forensic pathology applies medical knowledge to investigate causes of death, particularly in cases where legal issues may arise.