Definition:
Biogenesis is the scientific principle that living organisms are produced only by other living organisms and not from non-living matter. It counters the theory of spontaneous generation, advocating that all life forms originate from pre-existing life. This concept is fundamental to biology and supports the understanding of life’s continuity and the processes of reproduction and genetic inheritance.
Etymology & Origin:
The term “biogenesis” is derived from the Greek words “bios” meaning “life” and “genesis” meaning “origin” or “creation.” It literally translates to the “origin of life.” Coined in the 19th century, the concept of biogenesis was critical in establishing the basis for modern biology and understanding the complex processes that lead to the formation of new life from existing organisms.
Examples:
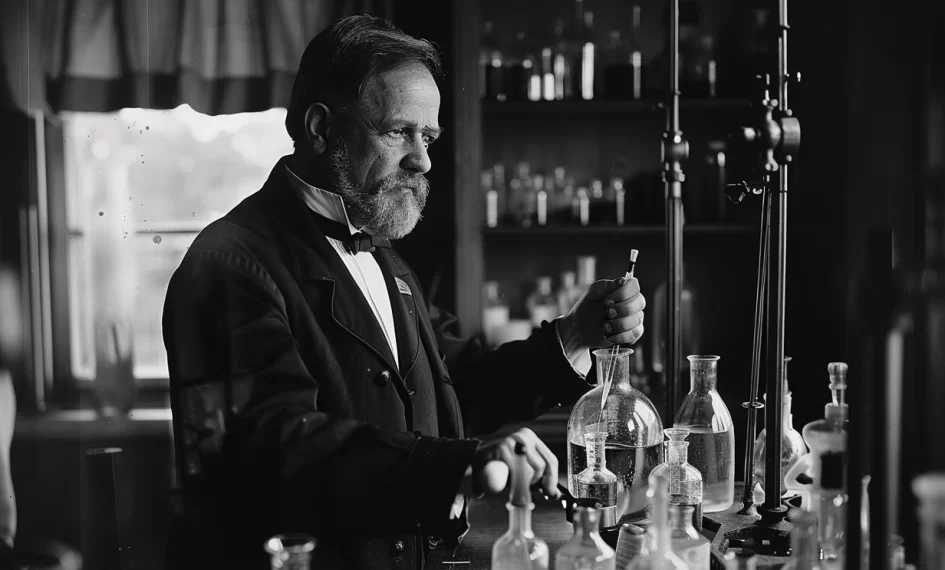
- The experiments of Louis Pasteur in the 19th century provided empirical support for biogenesis, demonstrating that microorganisms could not originate from non-living material.
- Biogenesis explains how plants produce seeds that grow into new plants, continuing the cycle of life.
- The study of cellular division and reproduction in animals and humans is a direct application of the principle of biogenesis, showing how life begets life.