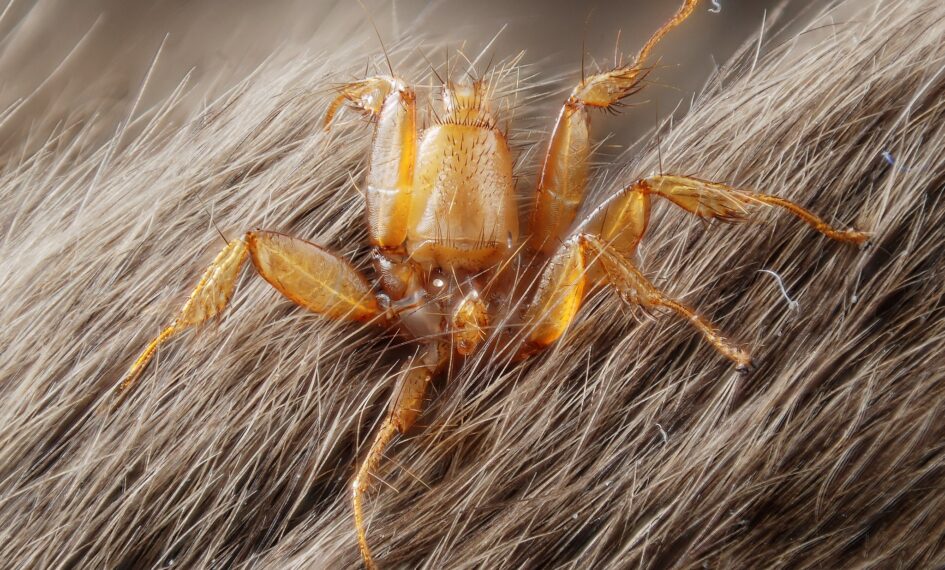
Definition of Parasite: A parasite is an organism that lives on or in a host organism and gets its sustenance at the host’s expense. Parasites vary widely and can include plants, animals, and fungi. Some cause little harm to their hosts, while others can be debilitating or even lethal. In a broader social context, the term “parasite” is also used metaphorically to describe individuals who exploit others for personal gain without reciprocation.
Revised Etymology and Origin: The term “parasite” derives from the Greek word “παράσιτος” (parasitos), a compound of “παρά” (para), meaning “beside” or “near,” and “σῖτος” (sitos), meaning “food” or “grain.” In ancient Greek society, a parasitos referred to a person who ate at the table of another, often in exchange for providing services like entertainment or flattery. While initially, the term might have had a more neutral connotation, it eventually gained a negative meaning, describing someone who sponges off others.
- Greek Roots: In its Greek origin, the term encapsulated the idea of living at the expense of another, which could be seen as a form of social sycophancy or dependence.
- Latin and English Adoption: The word was adopted into Latin as “parasitus,” where it continued to evolve. In English, “parasite” predominantly acquired its biological meaning, referring to an organism that lives in or on a host organism, deriving its nutrients at the host’s expense, often harmfully.
Thus, the term “parasite” has maintained its core meaning from ancient Greek to modern times, but with an increasingly negative connotation, shifting from a social freeloader to a biological entity that lives at the expense of its host.