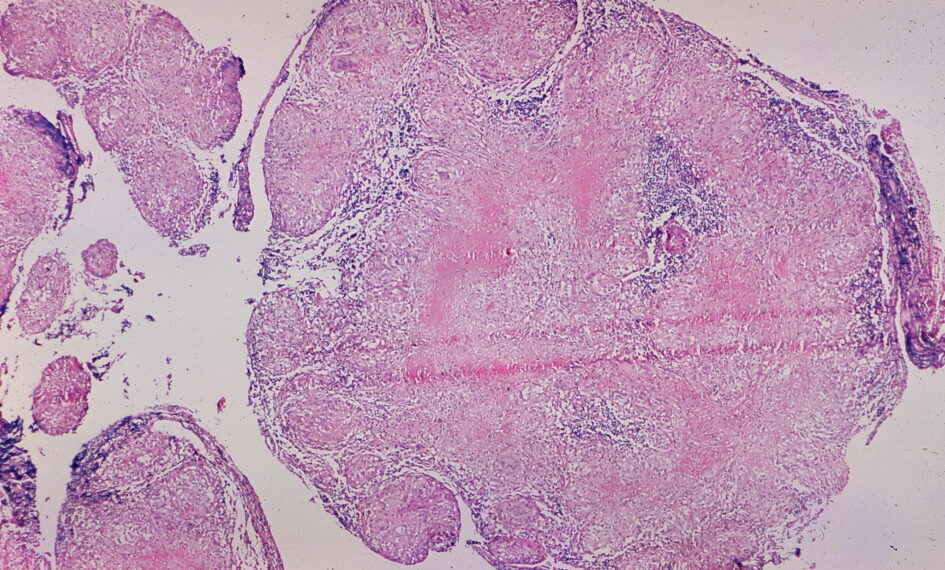
Definition of Sarcoidosis: Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease that affects multiple organs in the body, primarily the lungs and lymph glands. In people with sarcoidosis, abnormal masses or nodules called granulomas, consisting of inflamed tissues, form in certain organs of the body. These granulomas may alter the normal structure and possibly the function of the affected organ(s). The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown, and it can appear in any age group but typically affects people between 20 and 40 years of age.
Etymology and Origin: The term ‘sarcoidosis’ comes from the Greek words ‘sark-‘, meaning ‘flesh’, and ‘-oid’, meaning ‘like’, combined with the suffix ‘-osis’, which signifies a process or pathological condition. Essentially, it refers to a condition that produces flesh-like tissue growths. The term was first used in 1909 by the dermatologist Dr. J.H. Hutchinson, who described the skin lesions of the disease as “sarcoid”.