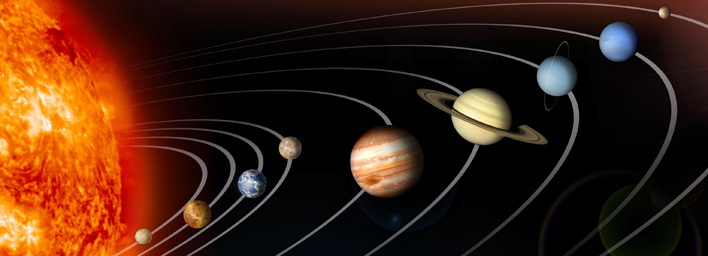
Definition: Heliocentric refers to a model of the solar system or universe where the sun is at the centre, with planets, including Earth, orbiting around it. This model contrasts with the geocentric model, which places Earth at the centre.
Etymology & Origin: The term ‘heliocentric’ comes from the Greek words ‘helios,’ meaning ‘sun,’ and ‘kentron,’ meaning ‘centre.’ It was popularized in the 16th century with the work of Nicolaus Copernicus, who proposed the heliocentric model in his seminal work “De revolutionibus orbium coelestium.”
Examples:
- The heliocentric model revolutionized astronomy by challenging the long-held geocentric view and laying the foundation for modern celestial mechanics.
- Galileo Galilei’s observations of Jupiter’s moons provided strong evidence supporting the heliocentric theory.
- The acceptance of the heliocentric model marked a significant shift in scientific thinking during the Renaissance, influencing the work of later astronomers like Kepler and Newton.